We know that the majority of ІТ employees are men, and women are still forming a minority. According to Zippia, only 34.4% of women make up the labor force in US tech companies like Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google та Microsoft. This is due to gender stereotypes about ІТ as a male-dominated industry. However, these stereotypes are gradually fading away and changing in a positive direction.
Despite the obvious sexism, modern women successfully influence ІТ industry, including extended reality and other immersive technologies. To illustrate this influence, we’ll present 5 famous women, who are ruling in XR industry.
Empowering Women in XR
In the 19th century, famous mathematician Ada Lovelace worked on Charles Babbage’s first mechanical computer and wrote the first algorithm for the machine. And in the 20th century, Austrian-Ukrainian-born Hollywood actress Hedy Lamarr, along with composer George Antheil, pioneered an Allies torpedoes radio system during World War 2. It became a prototype for modern wireless technologies, like Bluetooth, GPS, and Wi-Fi.
Get ready for more information about outstanding women that became the next Ada Lovelace and Hedy Lamarr in modern XR technologies.
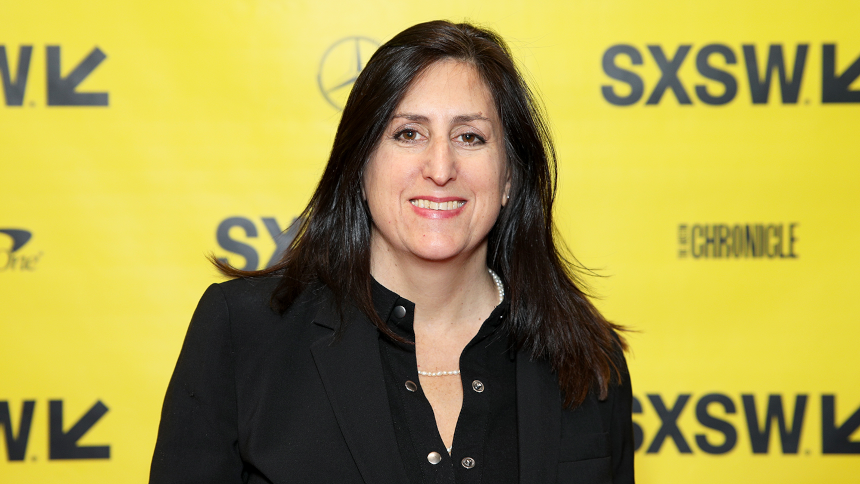
Image: SXSW
Nonny de la Pena, Godmother of VR
Nonny de la Pena was awarded the title “The Godmother of virtual reality” by top online media like Forbes, The Guardian, and Engadget. She’s a journalist, VR documentaries director, and the founder and CEO of Emblematic Group, which develops VR/AR/MR content.
The greatest merit of de la Pena is that she invented immersive journalism. Nonny de la Pena showcased her first VR documentary, The Hunger in Los Angeles, in the Sundance movie festival, back in 2012. You can read more about de la Pena’s most famous works in our previous article about VR in journalism.
In March 2022, de la Pena was one of the 16 Legacy Peabody Awards recipients for her work and influence in modern journalism. In her acceptance speech, she reminded about the importance of immersive technologies and what advantages they offer to modern journalism, using her joint project with Frontline After Solitary as an example. The VR experience is based on the true story of Kenny Moore, who spent many years in a solitary confinement cell in the Maine State Prison.
“When we did a piece in solitary confinement with Frontline, we did scanning of an actual solitary confinement cell. Well, now you’re in that cell. You’re in that room. And it has a real different effect on your entire body and your sense of, “Oh my God. Now I understand why solitary confinement is so cruel and unnecessary”. And you just can’t get that feeling reading about it or looking at pictures.”
De la Pena’s accounts in social media:
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/nonny-de-la-pe%C3%B1a-phd-4363644/
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nonnydelapena/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/ImmersiveJourno
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/nonny.delapena/
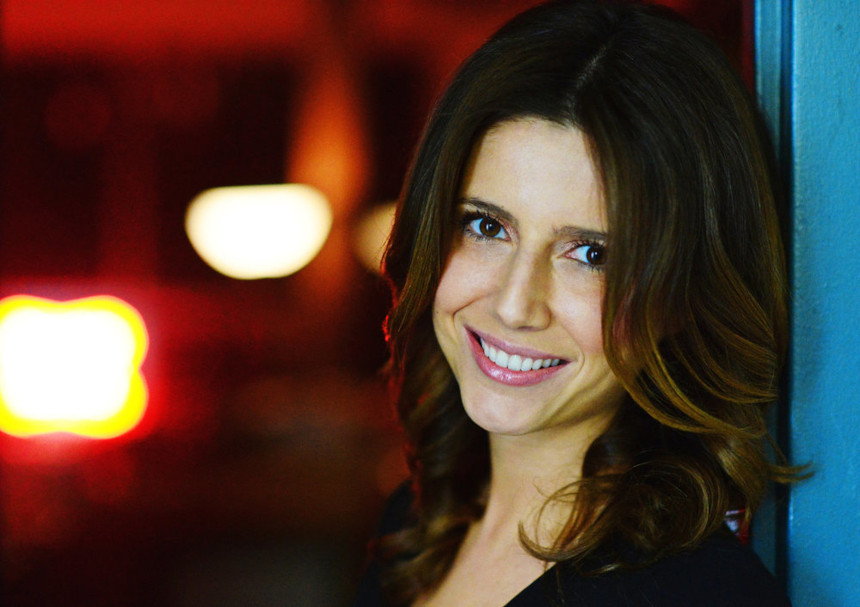
Image: LinkedIn
Dr. Helen Papagiannis, Experienced AR Expert
Dr. Helen Papagiannis works in augmented reality field for 17 years. Papagiannis is a founder of XR Goes Pop, which produced immersive content for many top brands including Louis Vuitton, Adobe, Mugler, Amazon, and many more. Particularly, they designed VR showroom for Bailmain, where you can see virtual clothes and accessories from a cruise collection on digital models, plus behind the scene videos.
Virtual try-on and shops are successfully applied by fashion brands, because they allow a customer to try on digital clothes before buying real one. You can read more about it here.
Doctor Papagiannis constantly gives her TED Talks and also publishes her researches for well-respected media like Harvard Business Review, The Mandarine, Fast Company, etc.
In 2017, the scientist and developer published a book called Augmented Human. According to Book Authority, it is considered to be the best book about augmented reality ever released. Stefan Sagmeister, designer, and co-founder at Sagmeister & Walsh Inc, thinks Augmented Human is the most useful and complete augmented reality guide, that contains new information about the technology, methods, and practices, that can be used in work.
Dr. Papagiannis’s accounts in social media:
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/hpapagiannis/
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/arstories/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/ARstories
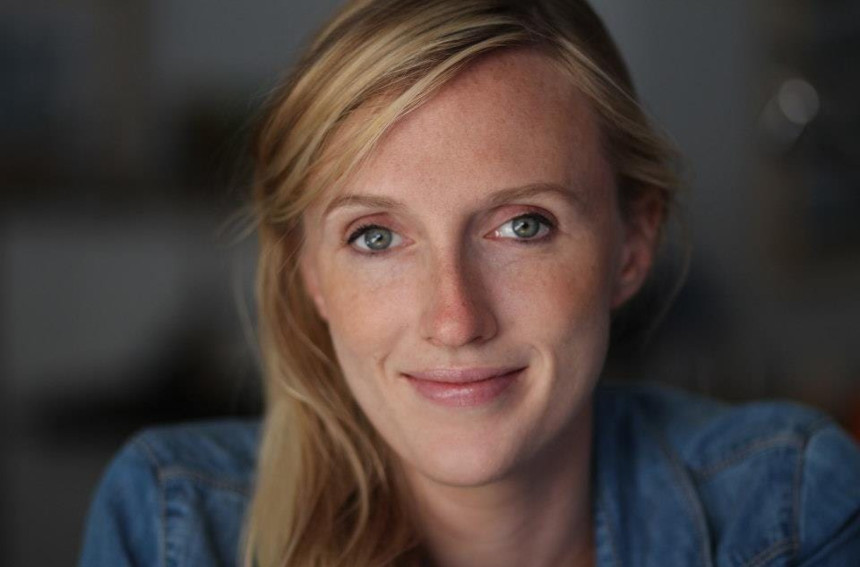
Image: Medium
Christina Heller, Trailblazer of Extended Reality
Christina Heller has 15 years of experience in XR. Huffington Post included her in the top 5 of the most influential women who are changing VR.
Heller is a founder and CEO of Metastage, that develops XR content for various purposes: VR games, AR advertisements, MR astronaut training, etc. Since 2018, Metastage has collaborated with more than 200 companies including H&M, Coca-Cola, AT&T, NASA, and worked with famous pop artists like Ava Max and Charli XCX.
Speaking about Heller herself, before Metastage she had worked in VR Playhouse, which immersive content was showcased at Cannes Film Festival, Sundance, and South by Southwest.
Under Christina Heller leadership, Metastage extended reality content was widely acclaimed and received many awards and nominations, including two Emmy nominations. Moreover, Metastage is the first US company, that officially started using Microsoft Mixed Reality Capture. This technology provides photorealistic graphics of digital models, using special cameras. And these cameras capture a human movement in a special room, where XR content is superimposed.
“It takes human performances, and what I like about it most is that it captures the essence of that performance in all of its sort of fluid glory, including clothing as well, said Heller. And so every sort of crease in every fold of what people are wearing comes across. You get these human performances that retain their souls. There is no uncanny valley with volumetric capture.”
Christina Heller’s researches were published in “Handbook of Research on the Global Impacts and Roles of Immersive Media” and “What is Augmented Reality? Everything You Wanted to Know Featuring Exclusive Interviews with Leaders of the AR Industry” (both 2019).
Heller accounts in social media:
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/christinaheller/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/ChristinaHeller
Image: Twitter
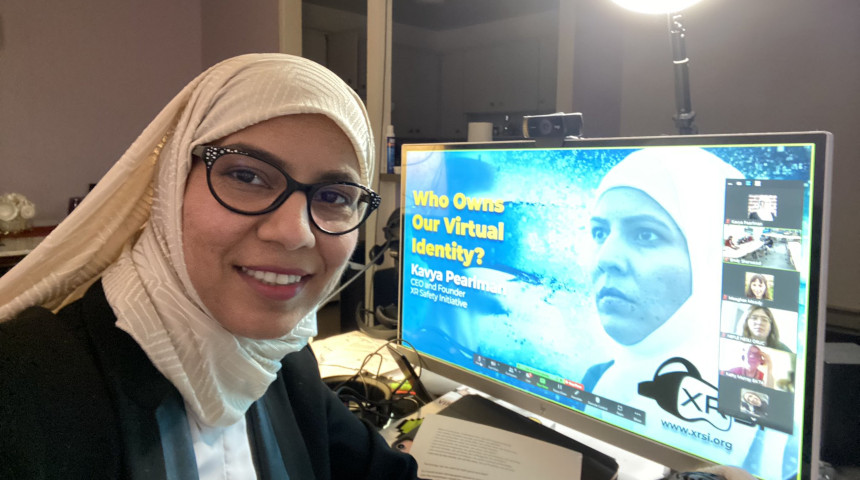
Kavya Pearlman, Cyber Guardian
Kavya Pearlman is called “The Cyber Guardian” and she is a pioneer in private data security with the use of immersive technologies, like metaverse. For three years in a row, from 2018 to 2020, and also in 2022, Kavya Pearlman was included in the top 20 Cybersafety influencers.
Pearlman is a founder and CEO of XR Safety Initiative, a non-profit company that develops privacy frameworks and standards of cybersecurity in XR.
Pearlman worked as a head of security for the oldest virtual world, Second Life. Basically, Kavya Pearlman was the first person who started considering ethical rules, data security, and psychology implications in the game and researched how bullying in VR can affect person’s mental state.
During The US Presidental election in 2016, Pearlman worked with Facebook as an advisor on third-party security risks, brought by companies and private users.
Kavya Pearlman is a regular member of the Global Coalition for Digital Safety and is a part of Metaverse Initiative on World Economical Forum, representing XR Safety Initiative.
Pearlman accounts in social media:
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/kavya-pearlman/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/KavyaPearlman
Image: BCC
Cathy Hackl, Godmother of Metaverse
In the immersive technologies world, Cathy Hackl is known as “the godmother of the metaverse”. Hackl is a futurologist and Web 3.0 strategist that collaborates with numerous leading companies on metaverse development, virtual fashions, and NFT. For the last two years, Big Thinker has been including Cathy Hackle in the top 10 of the most influential women in tech.
Cathy Hackl is also a co-founder and the head of the metaverse department in Journey. The company works with such big names as Walmart, Procter & Gamble, HBO Max, Pepsico and so on. One of its latest use cases are Roblox VR platforms Walmart Land and Walmart’s Universe of Play. In these platforms, players pass through different challenges, collect virtual merchandise, and interact with the environment.
Moreover, the futurologist and the metaverse specialist publishes science and analytic articles for top media, like 60 Minutes+, WSJ, WIRED, and Forbes.
Hackl also wrote four books about business in the metaverse and the technology development. The latest book, Into the Metaverse: The Essential Guide to the Business Opportunities of the Web3 Era, was published in January this year. On Amazon, the book has the highest rating — 5 stars out of 5. The book describes the metaverse concept at a very understandable and detailed level and is itself a quick read.
Hackl accounts in social media:
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cathyhackl/
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/cathyhackl/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/CathyHackl
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HacklCathy/
Qualium Systems appreciates inclusion and respects contributions made by women in XR, metaverse, and other immersive technologies every day. Moreover, our co-founder and CEO Olga Kryvchenko has been working in the IT field for 17 years already.
“It’s important for women to work in tech industries, and particularly in Immersive Tech, because it helps break down barriers and empowers women to pursue careers in fields that may have traditionally been male-dominated”, said Kryvchenko. “When women have more representation in tech, it creates a more welcoming and inclusive environment for future generations of women in the industry. Additionally, having a diverse workforce leads to better decision-making, as different perspectives and experiences are taken into account, ultimately resulting in better products and services for everyone.”